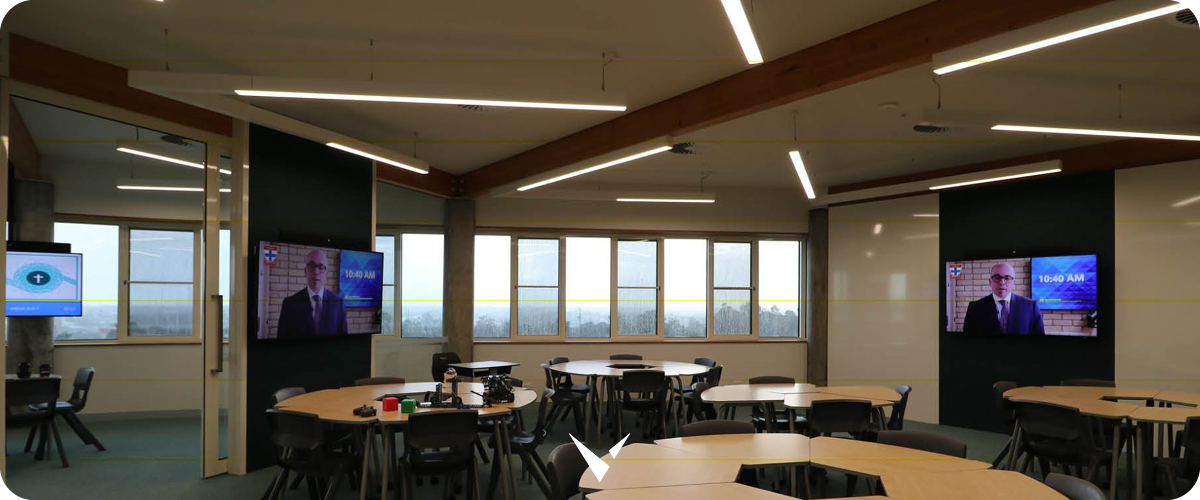
A technology-enabled active learning space (TEAL) is designed to bring technology right to the heart of learning. It’s an opportunity to establish the perfect learning environment for students.
But what should it look like and how do you make sure you get it right? In this post, we look at the key components of a successful TEAL classroom.
1. Flexibility
By its very definition, active learning means taking a variety of different approaches to learning. Whether it’s case studies, group tasks, debates or problem-solving scenarios, you’ll need to ensure the room layout and technology support the activities you have planned. To achieve that, you’ll need to retain a deal of flexibility in the way the room can be set up. The more adaptable the space, the more it will enable active learning.
2. Make the most of wall space
In a TEAL learning environment, the desks tend to be arranged in groups around the perimeter, with plenty of space in the centre for the lecturer to move around. With the room set up in this way, you’ll want to encourage collaboration and teamwork but, for it to work, you’ll need tools like whiteboards to allow the groups to record the key points from their discussions. One excellent way to achieve this—used in the TEAL room at New Mexico State University—is to cover every wall in the room in whiteboard paint.1
3. Projectors
The TEAL room is likely to be much bigger than a standard classroom—in many cases, they can cater for almost 100 students. As such, projectors (or screens) are an essential communication tool. They’ll be a way to display content from the lecturer—perhaps the key information required for the group to perform the task—and they’ll also be critical if each group is to share their findings with the rest of the room.
4. Screen-mirroring devices
With potentially as many as ten groups, you’ll want to be able to hand control of what’s being displayed on each projector screen—usually the wall—to any group seamlessly. Some TEAL environments have a certain number of laptops on each group table that are already connected to the projector or television screen. But the ultimate in flexibility is to allow students to use their own devices to connect to displays and present to one, some, or all of the screens in the room. To make that work, you need a screen-mirroring tool like Vivi.
5. Plugs
Lots of them. By its very nature, a TEAL room will contain plenty of electronic devices. During the planning process, it should be relatively straightforward to ensure there are sufficient sockets for everything you have planned. But you also need to make sure the room is future-proofed. Such is the pace of technological change that your class may well be using devices like virtual reality headsets within the next decade. Make sure that the room has the capacity to adapt.
6. Training
This is possibly the most important part of establishing a TEAL room and one that would be easy to overlook. Any technological implementation only succeeds if users quickly see benefits from using it and it’s the same with a TEAL classroom. After making a significant investment in creating the space, a school or university needs to make thorough training accessible to all who are likely to use the room.
Of course, you’ll want also want the ‘wow’ factor. A TEAL space really is very different from any classroom a student is likely to have used before. When they walk in for the first time, you’ll want to leave a lasting impression that really makes them want to learn.